Thyroid Treatment
Thyroid treatment depends on the specific thyroid condition a person has. The two most common thyroid conditions are hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
Here’s an overview of the treatments for each:

Hypothyroidism Treatment:
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. The most common treatment is synthetic thyroid hormone replacement therapy, which involves taking a medication called levothyroxine. Levothyroxine is identical to the natural thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) and helps to restore the hormone levels in the body.
Treatment for hypothyroidism is usually lifelong, and the dosage of levothyroxine may need to be adjusted over time based on the individual’s response and periodic blood tests to monitor thyroid hormone levels.
Hyperthyroidism Treatment:
Hyperthyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland produces excessive thyroid hormones. There are several treatment options for hyperthyroidism, and the choice of treatment depends on the cause, severity of symptoms, and the patient’s age and overall health.
Common treatments include:
- Antithyroid Medications: Medications such as Methimazole and Propylthiouracil (PTU) can be used to reduce the production of thyroid hormones. These drugs are often used as the first-line treatment for mild to moderate hyperthyroidism.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: Radioactive iodine is taken orally, and it is absorbed by the thyroid gland, where it helps to destroy the overactive thyroid cells. This treatment is often used when antithyroid medications do not effectively control the condition.
- Beta-Blockers: These medications do not treat the underlying cause of hyperthyroidism, but they can help manage some of the symptoms such as rapid heart rate, tremors, and anxiety.
d. Surgery (Thyroidectomy): In some cases, particularly when there is a large goiter, nodules, or the presence of thyroid cancer, surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland may be recommended.
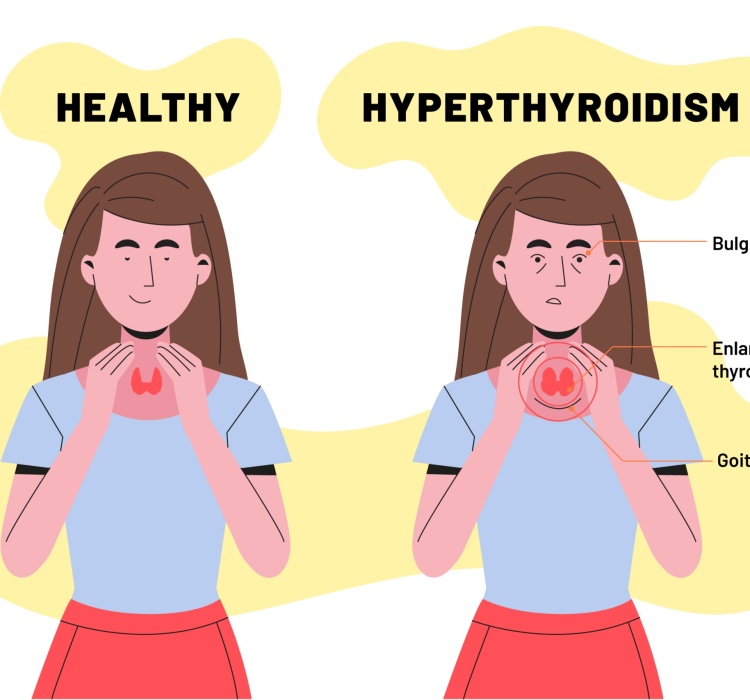
Thyroid treatment is typically managed by an endocrinologist, a doctor who specializes in hormonal disorders. And the problem can be cured with the help of homoeopathy. It’s important to note that the treatment plan may vary from person to person, and regular follow-up with the healthcare provider is crucial to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and make any necessary adjustments. Additionally, for thyroid cancer and more complex cases, the treatment approach may involve a combination of therapies, including surgery, radioactive iodine, and hormone therapy.









