Ankylosis Spondylitis Treatment
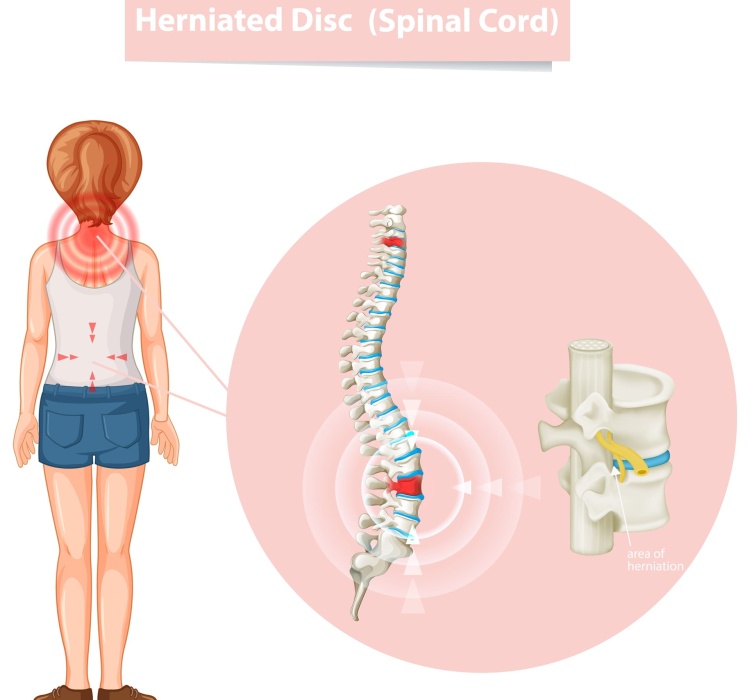
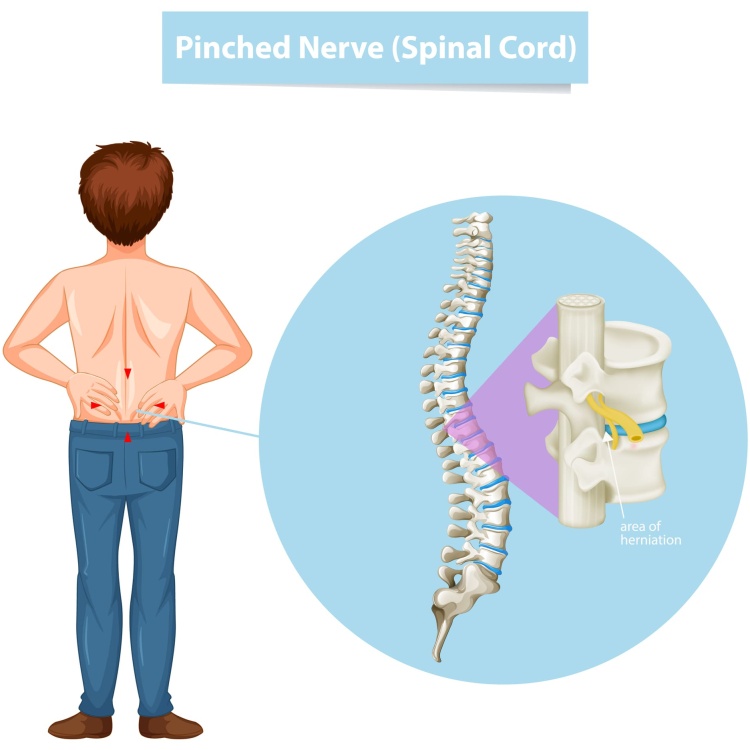
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects the spine, causing pain, stiffness, and eventually, fusion of the vertebrae. While there is no cure for AS, several treatment options can help manage the symptoms, improve quality of life, and slow down the progression of the disease. The treatment plan for AS typically involves a combination of medications, exercise, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments. In severe cases, surgery may be considered.
Here are some common treatments for ankylosing spondylitis:
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):
NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or diclofenac, are often the first-line medications used to reduce pain and inflammation associated with AS. They can help improve symptoms and increase mobility.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs):
DMARDs, such as sulfasalazine or methotrexate, may be prescribed for more severe cases or when NSAIDs alone are insufficient in controlling the inflammation and progression of AS.
Biologic Therapies:
Biologic medications, also known as biologics, are a class of drugs that target specific inflammatory pathways in the immune system. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, such as adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab, are commonly used biologics for AS. Other biologics like secukinumab, ixekizumab, and certolizumab pegol that target different molecules involved in inflammation have also shown effectiveness in AS treatment.
Physical Therapy and Exercise:
Regular physical therapy and exercise play a crucial role in managing AS. Physical therapy can help improve flexibility, posture, and muscle strength, while exercise can reduce pain, increase mobility, and maintain joint health. Low-impact activities such as swimming and cycling are often recommended.
Posture and Mobility Aids:
Devices like lumbar rolls or back braces can help maintain proper posture and reduce strain on the spine. Assistive devices such as canes or walking sticks may be useful during times of increased pain or stiffness.
Heat and Cold Therapy:
Applying heat pads or taking warm baths can help ease muscle tension and reduce pain. Cold packs may be used to reduce inflammation during flare-ups.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Making lifestyle adjustments, such as quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, can be beneficial in managing AS symptoms.
Surgical Intervention:
In severe cases where AS has caused significant spinal deformities or impaired mobility, surgery may be considered to correct the spinal alignment or replace damaged joints.
It’s important for individuals with ankylosing spondylitis to work closely with their healthcare provider, usually a rheumatologist, to develop a personalized treatment plan. Regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor disease progression, adjust treatments as needed, and ensure the best possible management of AS symptoms.
In homoeopathy the problem can be cured.









